
LATEST NEWS & PUBLICATIONS
Prediction and functional characterization of transcriptional activation domains
Mahatma et al. leveraged a neural network approach to systematically predict transcription factor activation domains. The findings further highlight the importance of aromatic and negatively charged amino acids and reveal the importance of unknown amino acid properties.

Functional Annotation of Proteins for Signaling Network Inference in Non-Model Species
Van den Broeck et al. developed a multi-layer neural network that annotates proteins by determining functionality directly from the protein sequence and enabled de novo identification of kinase-substrate interactions. The authors showed that the functional prediction neural network is scalable to other model and non-model species.

Establishing a Reproducible Approach to Study Cellular Functions of Plant Cells with 3D Bioprinting
Van den Broeck et al. established a framework for 3D bioprinting plant cells to study cell viability, cell division, and cell identity. The framework established paves the way for a general use of 3D bioprinting for studying cellular reprogramming and cell cycle reentry toward tissue regeneration.
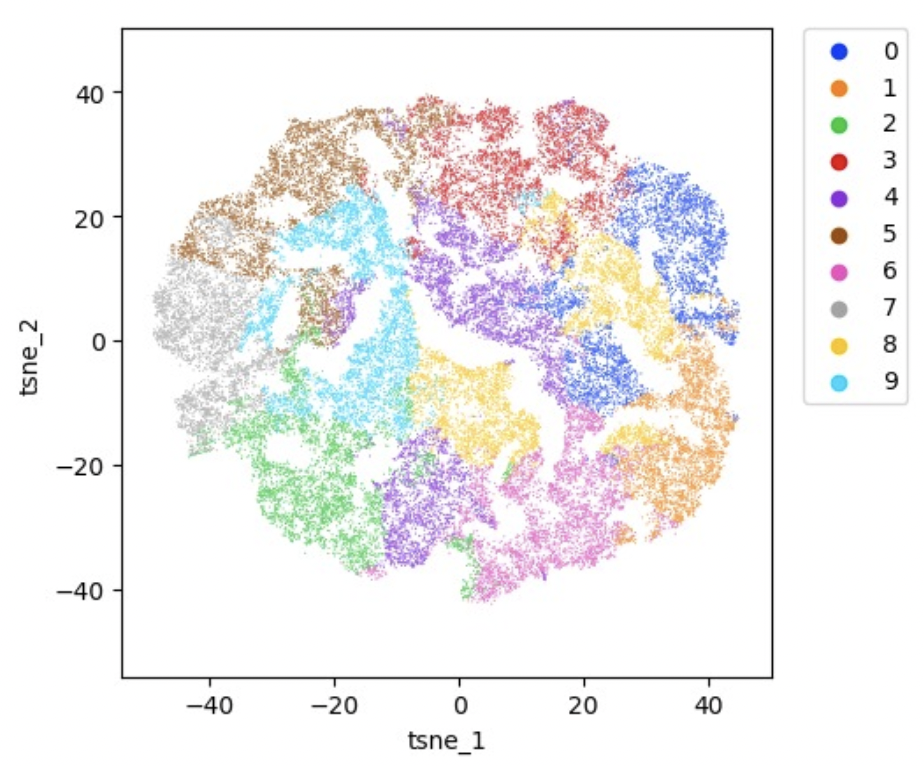
Single-Cell Genomics Revolutionizes Plant Development Studies Across Scales
This review highlights some of the technical developments and how they have led to profiling single-cell genomics in various plant organs. Zhu et al. emphasize the contribution of single-cell genomics in revealing developmental trajectories among different cell types within plant organs and present efforts toward comparative analysis of tissues and organs at a single-cell level.
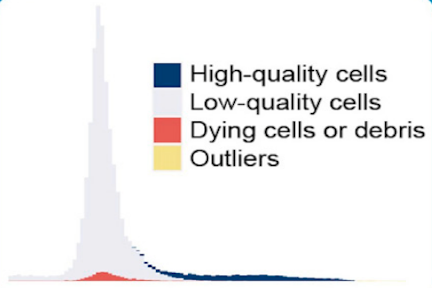
Protocol for Fast scRNA-seq Raw Data Processing Using scKB and Non-Arbitrary Quality Control with COPILOT
Hsu et al. describe a protocol to perform fast and non-arbitrary quality control of single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) raw data using scKB and COPILOT. This protocol streamlines the processing workflow and provides an easy entry for new scRNA-seq users.

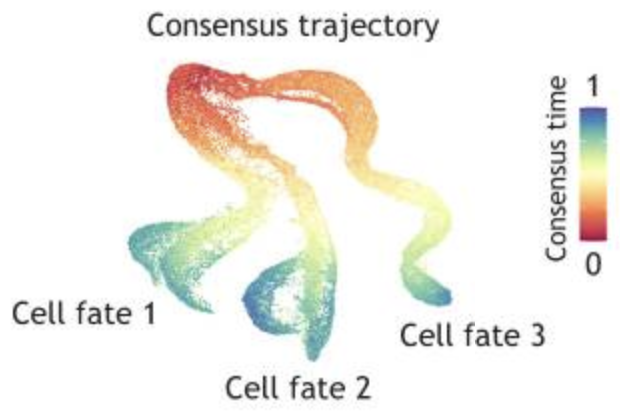
A Single-Cell Arabidopsis Root Atlas Reveals Developmental Trajectories in Wild-Type and Cell Identity Mutants
Using scRNA-seq, Shahan and Hsu et al. produced an Arabidopsis root atlas, revealing gradual gene expression changes underlying differentiation of cell types and candidate regulators of cell fate. The atlas enabled interpretation of smaller scRNA-seq datasets and revealed new phenotypes in developmental mutants.
